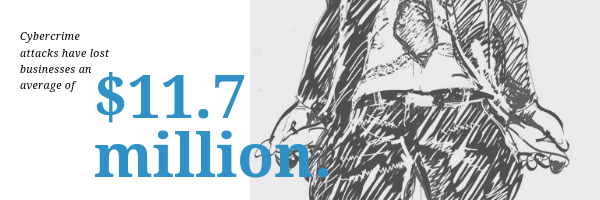What is HTTPS and SSL?
Let’s start by breaking down the term “secure site.”
At its core, a secure site is a website equipped with secure servers, through SSL, that allows you to send the website owners information without the risk of hackers stealing it.
So, what is SSL?
It is the required certificate that you must obtain from a licensed certificate provider before your website can be changed to an https. When an SSL session is made active, the information that is sent from any computer to the website owners will be changed from plain text that anyone can read to a unique coding that can only be understood by the sending and final destination computers. This makes it difficult for average people to hack into the private information of your website. This active SSL session is where the added s in https comes from. Although it technically stands for “Hypertext Transfer Protocol with Secure Sockets Layer,” most people shorten it to Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure or simply “https.”
Although this simple addition does not seem like much, there are some key elements of this that make it almost vital to the success of businesses.
Why Should I Care?
For businesses who plan on collecting any type of information through their website, making it secure is vital for the privacy of their customers. In order to understand the danger of an insecure website, it is important to understand that when someone goes to a website, everything they do or enter is sent from their server, across several other servers, before ever making it to the targeted location. All that is needed for one of the computers along the way to steal the information sent is a packet sniffer that can be downloaded free on any laptop. This makes it easy for anyone to steal website information quickly.
Where the secure element comes in is by taking all of the information from easy to read plain text to encrypted codes. This means that although hackers may be able to get the information, they will have no idea what to do with it. If a company asks for information through an insecure site and that information is stolen, the company could face serious liability problems and can also lose the trust of their audience.
Hackers can also easily change unencrypted messages being sent from your website before it ever reaches the consumer.
This leaves your website, and more importantly your brand, open to the influence of any hacker. They can easily leave links, pictures, or ask for information that the client will associate with your website without you even realizing the change was made. They can even hijack the site entirely, giving them the opportunity to post whatever they want under your brand name. These cybercrime attacks have lost businesses an average of $11.7 million.
Some Benefits of a Secure Site
Some benefits that most companies don’t realize.
- Https sites on average load 334% faster than standard http
- They build brand loyalty and power by showing customers you are willing to go the extra mile to keep them safe.
- It is said that Google uses site security as one of its search ranking factors.
With all this in mind, the key takeaway is that secure sites are necessary because they provide safety for your clients, integrity for your website, and globally recognized authentication of the two.
Google, Secure Sites, and the SEO Impact
Many people exploring https for the first time wonder why Google cares so much about website security and what the company does to sites that are not secure. Google cannot outrite block the websites that are insecure because it would not be a proper search engine if that were the case. However,
Google has taken every other precaution possible to warn their users about insecure sites.
The reason for this grave concern is simply the way it affects Google’s brand image. Google strives for a quick and painless web search experience for every user, every time. Therefore, the prospect of users being linked to a site that may have false information, technical issues, or the possibility of security vulnerabilities is a risk Google does not want to take. Although the vulnerable website is not Google’s website, Google does not want to jeopardize user trust.
Google’s Changes to their (SEO) Page Rank Protocol
For this reason, changes to SEO (search engine optimization) protocol began around 2014. In the beginning, Google changed its SEO protocol slightly to favor companies that were secure. They also included a content-neutral information button that would warn customers not to share personal information on the insecure site.
This laid back approach did not work very well, so in January 2017, the first major change towards “punishing” insecure websites was made with the release of Chrome 56. This version contained URL warnings against non-secure sites that asked for any input such as passwords or credit card information. Businesses quickly saw an impact. The security warnings made more customers uneasy enough to leave the sites without risking any exposure.
This prompted many companies to make the switch. However, Google already had a much bigger plan in motion.
In 2018, all http sites were given this “Not Secure” warning label in the latest Google Chrome browser.
Although the future of these changes is still up in the air, some information has indicated that Google may plan to remove the lock symbol entirely in an effort to create an internet world in which, “users should expect that the web is safe by default.” This will also do further damage to the reputation of unsafe websites by making their security warnings stick out even more.
Overall, Google sums up their goal of this endeavor with the sentence, “Chrome’s new interface will help users understand that all http sites are not secure, and continue to move the web towards a secure https web by default.”
Make the Update
If your business website has not made the migration from “http” to “https,” now is the time to do it. It is a relatively easy, and inexpensive thing to do. Moving to a secure site could actually keep you from losing potential customers. And, really, who wouldn’t want to do that?